Understanding Public Administration and Policy
Public administration and policy are fundamental components of any functioning society, acting as the backbone of governmental operations and societal organization. They encompass the systems and processes through which government entities manage resources, implement laws, and deliver services to citizens. This intricate field involves a wide array of activities, from the strategic planning of national initiatives to the day-to-day management of public services, all aimed at fostering collective well-being and maintaining order. Grasping these concepts is crucial for understanding how decisions are made, how resources are allocated, and how societies are governed.
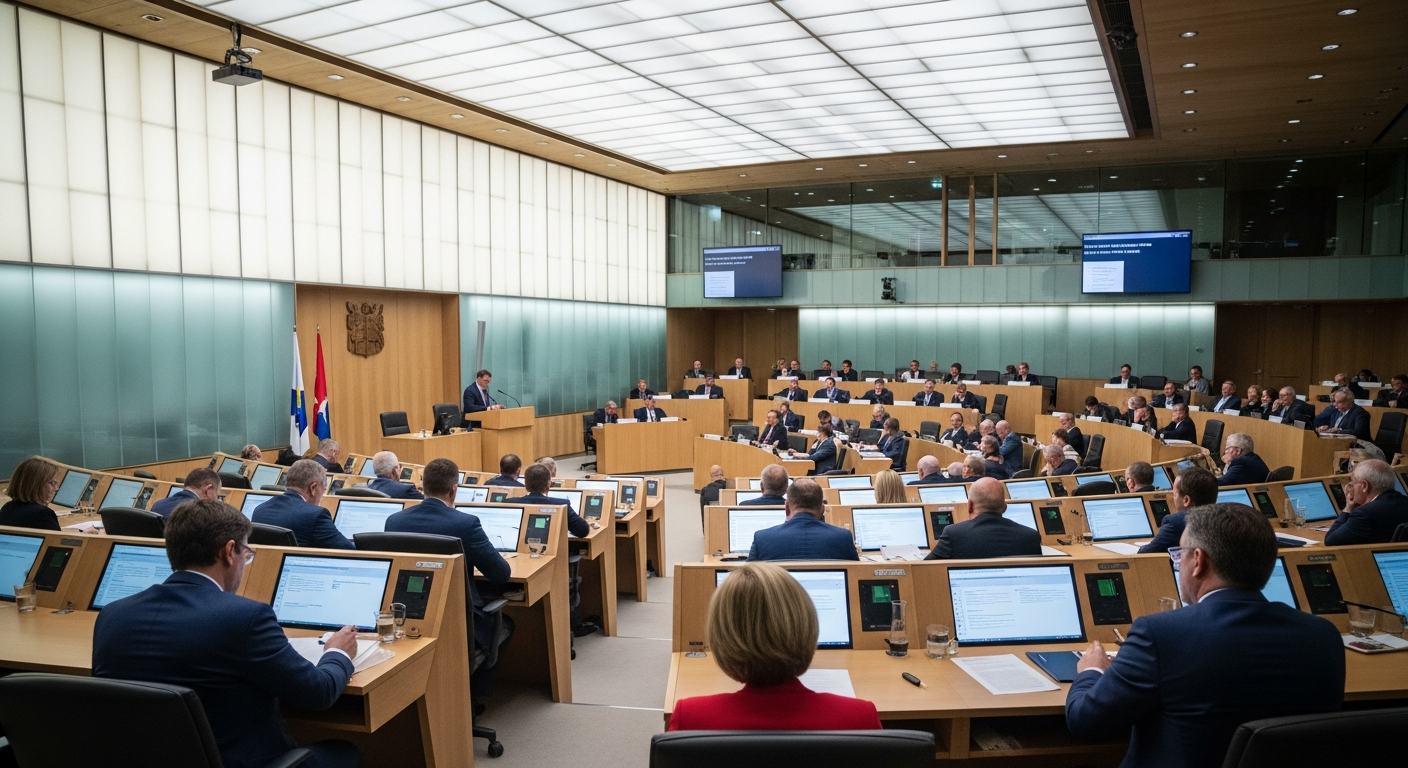

What is Public Administration?
Public administration refers to the implementation of government policy and also to an academic discipline that studies this implementation and prepares civil servants for working in the public service. It involves the organization and management of public programs and services, ensuring that government directives are carried out effectively. This field is essential for efficient governance, encompassing the activities of all government branches—executive, legislative, and judicial—as they fulfill their respective roles. It’s about how the bureaucracy functions to deliver on the promises and mandates set forth by political leaders, impacting everything from national defense to local sanitation services.
Effective public administration requires a deep understanding of organizational theory, public finance, human resource management, and ethical considerations. Administrators are tasked with translating broad policy goals into tangible actions, managing public resources responsibly, and providing services that meet the needs of diverse populations. Their work often involves navigating complex challenges, balancing competing interests, and ensuring transparency and accountability in all government operations.
Developing Public Policy and Legislation
Public policy represents the collective decisions made by governments to address societal issues. These policies can range from economic regulations to social welfare programs and environmental protection initiatives. The development of legislation is a critical step in formalizing these policies into enforceable laws. This process typically involves identifying a problem, formulating potential solutions, selecting the most appropriate course of action, and then implementing and evaluating its effectiveness.
Various stakeholders, including government agencies, interest groups, experts, and the public, often contribute to the policy-making process. Once a policy is formulated, it often goes through the parliament or legislative body for debate, amendment, and approval, eventually becoming a statute. These frameworks guide the actions of government bodies and citizens alike, aiming to create a structured and predictable environment for societal interaction and progress.
The Role of Regulation and Compliance
Regulation is a key tool in public policy, used by governments to influence behavior and achieve specific societal goals. It involves setting rules or standards that individuals, organizations, and industries must adhere to. The purpose of regulation can vary widely, from protecting public health and safety to promoting fair competition and environmental sustainability. These rules are often codified in legal texts and enforced by specific government agencies.
Compliance refers to the act of adhering to these regulations and statutes. For individuals and organizations, understanding and fulfilling compliance requirements is crucial to avoid penalties and operate within the bounds of the law. This area also heavily involves ethics, as regulatory bodies often establish ethical guidelines to ensure fair practices and prevent corruption. Regular audits and oversight mechanisms are typically in place to monitor compliance and ensure the integrity of public and private sector operations.
Ensuring Justice and Rights
The pursuit of justice is a cornerstone of democratic societies, ensuring fair treatment and the protection of individual rights. The judiciary plays a pivotal role in this, interpreting legislation and applying it to specific cases, thereby upholding the rule of law. The system of courts provides a forum for resolving disputes, prosecuting criminal offenses, and reviewing the legality of government actions. This branch of government acts as a crucial check on the powers of the executive and legislative branches, safeguarding constitutional principles.
Access to justice is a fundamental right, and legal systems are designed to provide mechanisms for redress when rights are violated. This includes provisions for legal aid, fair trials, and due process. The effectiveness of the judiciary in upholding rights and delivering justice is a critical indicator of a society’s commitment to fairness and equality, contributing significantly to public trust in governmental institutions.
Foundations of Democratic Governance
Democracy is a system of governance where citizens have the power to elect their representatives, who then make decisions on their behalf. The constitution serves as the supreme law of the land, establishing the fundamental principles, powers, and duties of government, and guaranteeing the rights of citizens. It provides the overarching framework within which all legislation and policy are developed and implemented. Understanding civics—the study of the rights and duties of citizenship—is essential for active participation in a democratic society.
Parliament (or similar legislative bodies) is where elected representatives debate and enact laws, representing the will of the people. This institution is vital for maintaining accountability and transparency in governance. The interplay between the constitution, parliament, and the active engagement of civics ensures a robust and responsive democratic system, continuously evolving to meet the challenges and aspirations of its populace.