Sustainable Development in Modern Housing Projects
Sustainable development in modern housing projects represents a fundamental shift in how residential spaces are conceived, designed, and constructed. It moves beyond merely erecting buildings to encompass a holistic approach that considers environmental impact, resource efficiency, and long-term community well-being. This paradigm focuses on creating living environments that are not only comfortable and aesthetically pleasing but also minimize ecological footprints and contribute positively to the surrounding ecosystem. As urban populations continue to grow globally, the imperative for such development becomes increasingly critical for fostering resilient and livable communities for future generations.
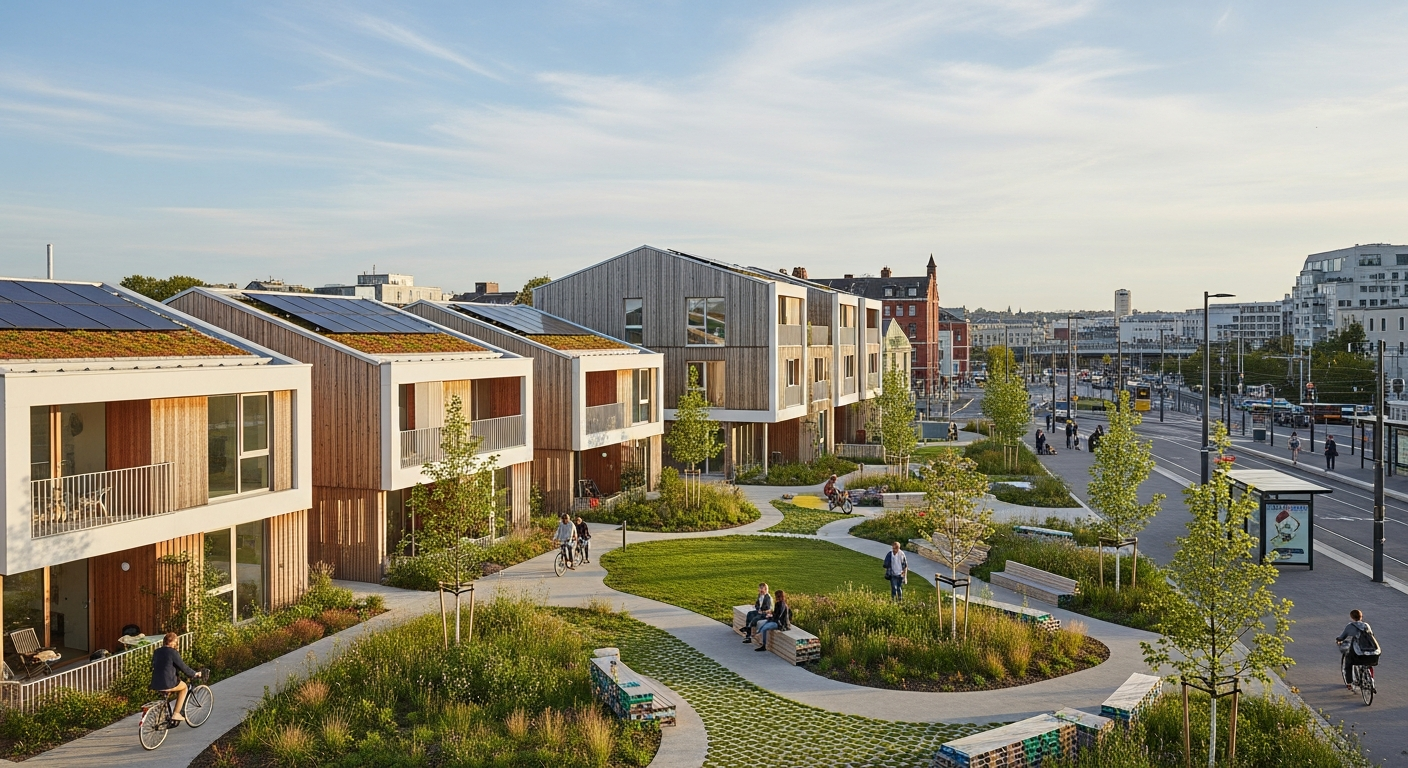

Understanding Sustainable Housing Development
Sustainable housing development fundamentally redefines the approach to creating residential property. It integrates environmental protection, social equity, and economic viability into every stage of the development process. This includes careful land selection, efficient use of materials, reduction of energy and water consumption, and the promotion of healthy indoor environments. The goal is to create housing that contributes to a higher quality of life for its occupants while minimizing adverse effects on the planet. This comprehensive view extends to the entire lifecycle of a building, from its initial planning and construction to its operation, maintenance, and eventual decommissioning.
Modern housing initiatives often prioritize features such as renewable energy sources, advanced insulation techniques, and smart home technologies to optimize resource use. These elements are crucial for reducing the operational costs of residential units and lowering their carbon emissions. The broader context of urban development plays a significant role, as sustainable housing projects are increasingly viewed as integral components of larger, eco-friendly communities that support walking, cycling, and public transportation, thereby reducing reliance on private vehicles.
Key Principles of Sustainable Urban Planning and Architecture
Effective sustainable development relies heavily on thoughtful urban planning and innovative architecture. Planning for sustainable zones involves creating mixed-use developments that integrate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, fostering vibrant communities and reducing commuting distances. Architects play a pivotal role in designing buildings that are energy-efficient, utilize sustainable materials, and maximize natural light and ventilation. This approach often involves passive design strategies that harness local climate conditions to enhance comfort and reduce energy demand.
Considerations for site-specific conditions, such as topography, solar orientation, and prevailing winds, are integrated into the architectural design to optimize building performance. The choice of construction materials is also critical, favoring those with low embodied energy, recycled content, and local sourcing to reduce transportation impacts. Green roofs, permeable paving, and rainwater harvesting systems are examples of features that contribute to ecological balance within the built environment, managing stormwater and enhancing biodiversity in residential areas.
Economic and Investment Trends in Green Property Markets
The global real estate market is increasingly recognizing the value of sustainable property assets. Investment in green housing projects is growing, driven by a combination of environmental awareness, regulatory incentives, and the potential for long-term financial returns. Property valuation methodologies are evolving to incorporate sustainability metrics, acknowledging that eco-friendly homes often command higher market prices and experience greater demand. This trend suggests a maturing market where sustainability is not just a niche but a significant factor influencing residential transactions.
Financing options for sustainable housing are also expanding, with various green mortgages and loan programs designed to encourage environmentally responsible development and ownership. For developers, constructing sustainable buildings can lead to reduced operating costs, lower vacancy rates, and increased asset longevity, making them attractive long-term investments. These market dynamics are reshaping how stakeholders perceive and engage with housing development, moving towards a future where environmental performance is a key differentiator.
Challenges and Future Directions in Sustainable Real Estate
While the momentum for sustainable development in real estate is strong, several challenges persist. These include the initial capital investment often associated with green technologies, which can be higher than conventional construction, although long-term savings typically offset these costs. Overcoming regulatory complexities and ensuring consistent standards across different urban zones also present hurdles. Additionally, educating both developers and consumers about the benefits of sustainable housing is essential for broader adoption.
Looking ahead, the future of sustainable real estate is likely to involve further innovation in materials science, smart city technologies, and modular construction techniques that reduce waste and increase efficiency. The integration of artificial intelligence and data analytics will play a larger role in optimizing building performance and energy management. Collaborative efforts between governments, private sector developers, and communities will be crucial in driving the widespread adoption of sustainable practices, ultimately shaping more resilient and environmentally conscious residential landscapes worldwide.