Sustainable Approaches in Food Cultivation
Sustainable food cultivation involves methods that are environmentally friendly, economically viable, and socially responsible. These approaches aim to produce food while conserving natural resources, reducing environmental impact, and ensuring long-term food security. It encompasses a wide range of practices from farm to fork, focusing on ecological balance and community well-being.
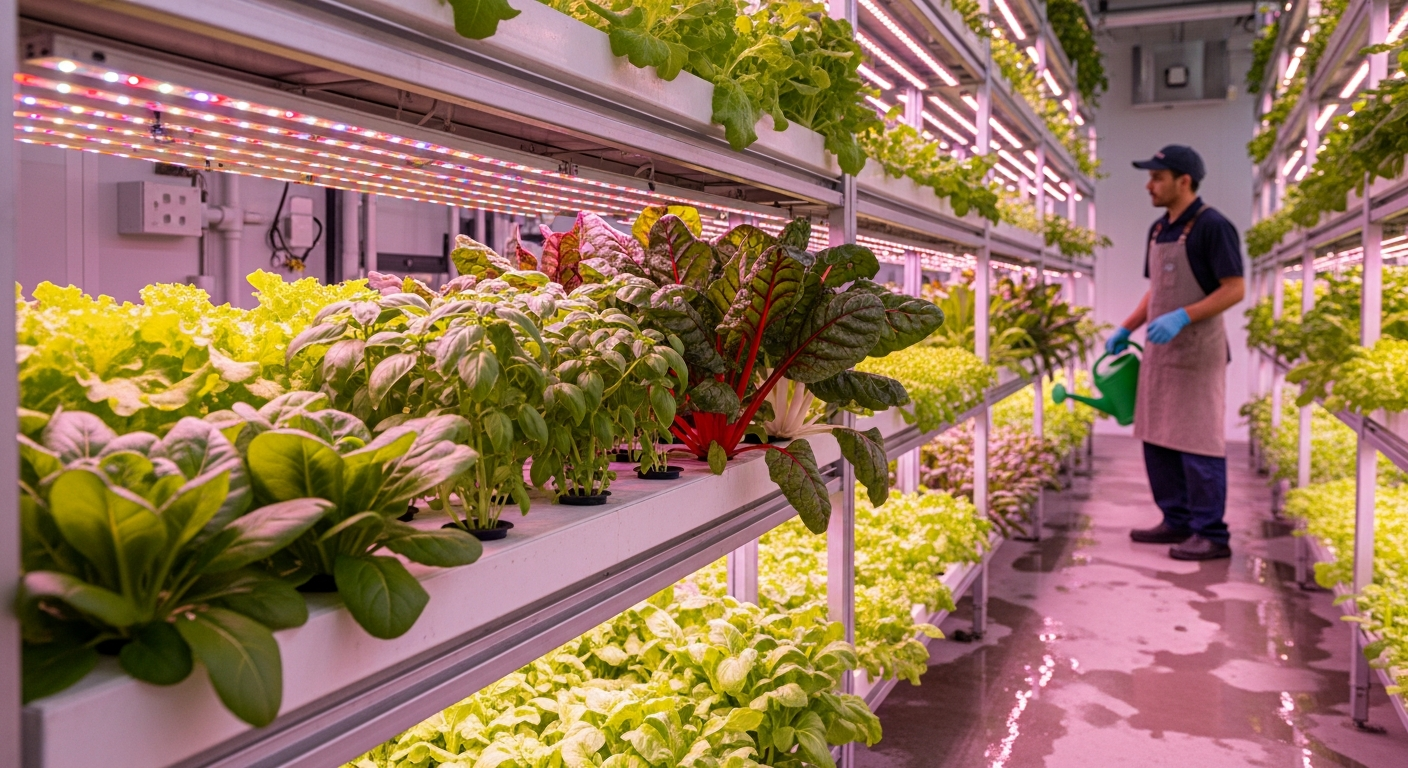

Sustainable food cultivation is a critical area of focus in modern agriculture, addressing the need to feed a growing global population without depleting the planet’s resources. It moves beyond conventional farming by integrating ecological principles, economic considerations, and social equity. This holistic perspective ensures that food systems can continue to thrive for future generations, fostering resilience against environmental challenges and promoting healthier communities worldwide. The shift towards sustainability is driven by an understanding of the interconnectedness between agricultural practices, environmental health, and human well-being.
What Defines Sustainable Food Production and Sourcing?
Sustainable food production and sourcing emphasize practices that minimize ecological footprints while maximizing efficiency and fairness. This includes reducing reliance on synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, promoting biodiversity through crop rotation and diverse planting, and conserving water resources through efficient irrigation techniques. Sourcing sustainably often involves supporting local farmers and producers who adhere to these environmentally conscious methods, thereby reducing transportation emissions and strengthening local economies. The focus is on creating closed-loop systems where waste is minimized, and resources are recycled, contributing to a more resilient and self-sufficient food system. These methods also consider the welfare of farm workers and ethical treatment of animals, if applicable, ensuring a comprehensive approach to production and sourcing that benefits all stakeholders.
Enhancing Nutrition and Health Through Sustainable Ingredients
Sustainable cultivation practices often lead to higher quality ingredients that can contribute significantly to nutrition and health. By nurturing soil health through organic matter and reduced chemical use, sustainably grown produce can offer a richer profile of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These practices support the natural biological processes in the soil, which in turn enhance the nutrient uptake of plants. Consumers who choose sustainably sourced foods are often selecting produce that has been grown with attention to ecological balance, potentially leading to food with fewer residues from synthetic chemicals. This connection between sustainable farming and nutrient density is a key driver for many individuals seeking to improve their dietary health and overall well-being.
Culinary Practices and Flavors in Sustainable Gastronomy
Culinary arts and gastronomy are increasingly embracing sustainable principles, moving towards menus that highlight seasonal, local, and ethically sourced ingredients. Chefs and home cooks alike are exploring innovative recipes and preparation methods that minimize food waste and celebrate the natural flavors of sustainably grown produce. This often involves techniques that preserve ingredients, such as fermenting or pickling, and utilizing every part of a plant or animal. The trend in sustainable gastronomy is not just about environmental responsibility; it’s also about rediscovering authentic tastes and creating a deeper connection between the diner and the origin of their food. From farm-to-table restaurants to home kitchens, the emphasis on sustainability is enriching the dining experience and expanding the palette of conscious consumers.
Global Trends and Cultural Impact of Sustainable Food
Across the global landscape, there is a growing recognition of the importance of sustainable food systems. This is reflected in various trends, such as the rise of plant-based diets, increased demand for organic products, and the resurgence of traditional farming methods that are inherently sustainable. Different cultures are adapting their food practices to incorporate sustainability, often drawing on ancestral knowledge of land stewardship and resource management. For example, indigenous agricultural systems frequently embody principles of biodiversity, ecological balance, and community collaboration. These global trends also highlight the need for international cooperation to address challenges like climate change, food waste, and equitable access to nutritious food, shaping a future where food culture is synonymous with environmental responsibility.
Promoting Wellness and Sustainable Diets
Adopting a sustainable diet is a significant step towards both personal wellness and environmental responsibility. Such a diet typically prioritizes plant-rich foods, reduces the consumption of resource-intensive products, and minimizes food waste. It encourages mindful eating and a deeper understanding of where food comes from and its journey to the plate. Beyond individual choices, promoting wellness through sustainable diets also involves advocating for policies that support sustainable agriculture, reduce food insecurity, and improve public health outcomes. This holistic approach to food and wellness recognizes that the health of individuals is intrinsically linked to the health of the planet, fostering a lifestyle that supports long-term vitality for both.
Sustainable approaches in food cultivation represent a fundamental shift in how humanity interacts with its food sources and the environment. By integrating ecological soundness, economic viability, and social equity, these methods offer a pathway towards a more resilient, equitable, and healthy food system for everyone. The continuous evolution of these practices, from production to culinary application, underscores a collective commitment to securing the future of food. The ongoing dialogue and innovation in this field are crucial for addressing complex challenges and building a world where food nourishes both people and the planet sustainably.