Protecting Human Rights Through Global Norms
Human rights are fundamental to the dignity and worth of every individual, forming the bedrock of just societies worldwide. The concept of human rights has evolved significantly, moving from philosophical ideals to a robust framework of international laws and global norms. This evolution reflects a collective commitment by nations to ensure basic protections and freedoms for all people, irrespective of their nationality, ethnicity, gender, religion, or any other status. Understanding how these global norms are established, implemented, and upheld is crucial for appreciating the intricate mechanisms that strive to safeguard universal human dignity.

How does international Legislation establish human Rights?
International human rights legislation serves as the primary mechanism for codifying and protecting fundamental rights globally. These laws are typically articulated in treaties, conventions, and covenants that are adopted by the United Nations and subsequently ratified by individual states. Key instruments include the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR). These documents outline a comprehensive set of civil, political, economic, social, and cultural rights that states are obligated to respect, protect, and fulfill. By ratifying these treaties, nations commit to incorporating their principles into domestic law and practice, creating a legal basis for individuals to claim their rights and for states to be held accountable.
What role does global Governance play in upholding Justice?
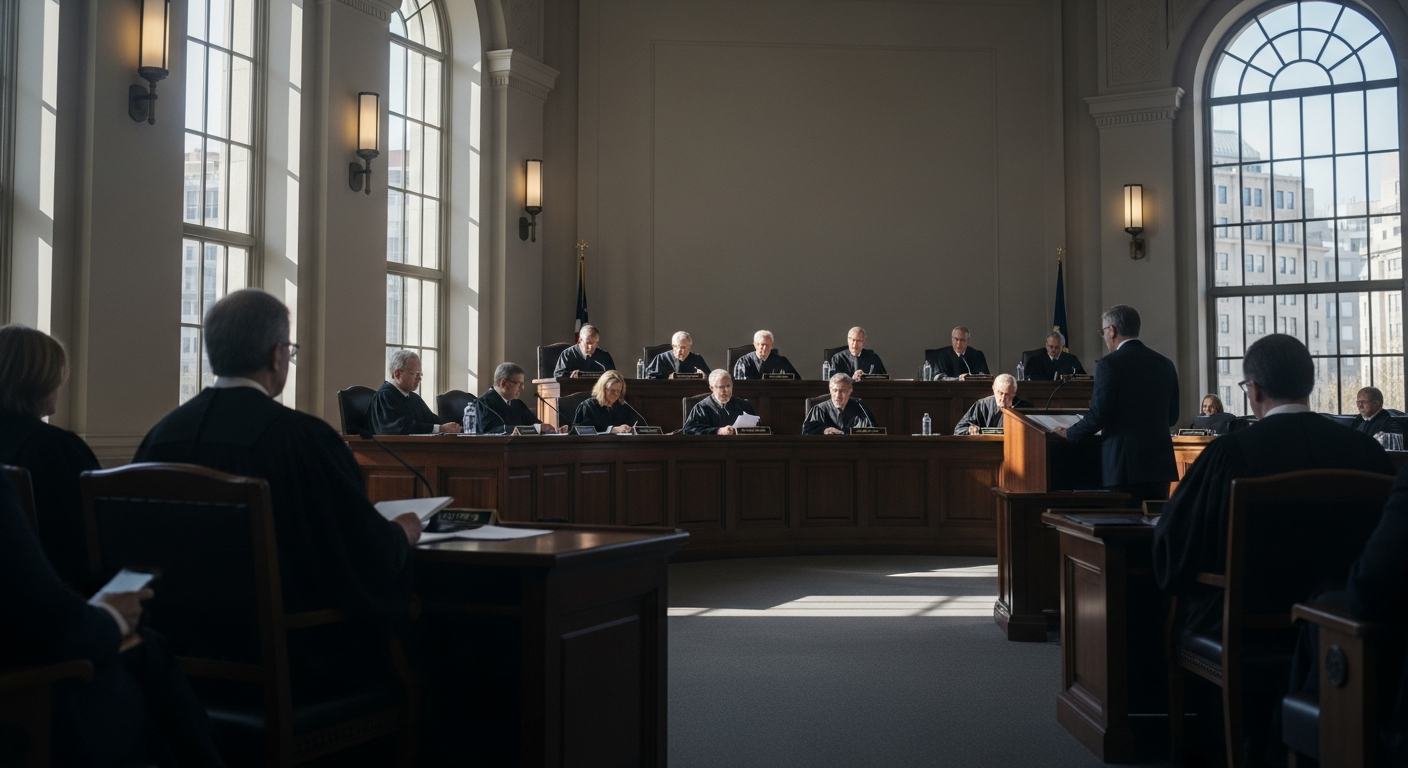
Global governance structures are essential for supervising the implementation of human rights standards and promoting international justice. Organizations like the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) and its various treaty bodies monitor states’ compliance with their human rights obligations. These bodies review country reports, conduct investigations, and issue recommendations to address violations. Furthermore, international courts, such as the International Criminal Court (ICC), play a critical role in prosecuting individuals for grave human rights abuses, including genocide, crimes against humanity, and war crimes. This multi-layered system of oversight and accountability aims to ensure that human rights violations do not go unaddressed and that victims can seek redress.
How do national Policy and Regulation support international human rights Frameworks?
At the national level, government policy and regulation are vital for translating international human rights frameworks into actionable domestic measures. This involves enacting laws that prohibit discrimination, guarantee freedom of expression, ensure fair trials, and provide access to education and healthcare. Governments are expected to establish institutions, such as national human rights commissions, to monitor the human rights situation within their borders, investigate complaints, and advocate for reforms. Effective national policies also include public awareness campaigns and educational programs to inform citizens about their rights and responsibilities, fostering a culture of respect for human dignity.
Ensuring Compliance and fostering Transparency in human rights Administration
Effective compliance with human rights obligations requires robust mechanisms for monitoring and reporting, coupled with a commitment to transparency in governmental administration. States are often required to submit periodic reports to international treaty bodies, detailing their efforts to implement human rights. These reports are subject to scrutiny, and civil society organizations often provide alternative reports, offering a broader perspective on the human rights situation. Transparency in governmental processes, including legislative debates, budget allocations, and policy decisions, allows for public oversight and helps to identify potential areas of concern or non-compliance. Open data initiatives and accessible legal information further empower citizens and civil society to hold governments accountable.
The Judiciary and Legal systems in protecting human rights and promoting Ethics
The judiciary and national legal systems are fundamental pillars in the protection of human rights and the promotion of ethics. Independent courts serve as crucial safeguards, providing avenues for individuals to seek remedies when their rights are violated. Judges interpret national laws in light of international human rights standards, ensuring that domestic legislation is consistent with global norms. The principle of the rule of law dictates that everyone, including those in power, is subject to the law, and that legal processes are fair and impartial. This judicial oversight is critical for upholding due process, ensuring equality before the law, and preventing abuses of power, thereby reinforcing a society’s ethical commitment to human rights.
The importance of Democracy and Public engagement in human rights
Democracy and active public engagement are intrinsically linked to the effective protection and promotion of human rights. Democratic systems, characterized by free and fair elections, separation of powers, and respect for civil liberties, provide the political space necessary for human rights to flourish. They enable citizens to participate in decision-making, express dissent, and hold their leaders accountable. Public engagement, through civil society organizations, media, and grassroots movements, plays a crucial role in advocating for human rights, raising awareness about violations, and influencing policy reforms. When the public is informed and empowered, it creates a powerful force for ensuring that human rights remain a priority in governance and societal discourse.
Protecting human rights through global norms is an ongoing and multifaceted endeavor. It requires continuous effort from international organizations, national governments, legal systems, and active citizens. The intricate web of international legislation, global governance mechanisms, national policies, and judicial oversight works together to build a framework that strives for universal dignity and justice. While challenges persist, the commitment to these global norms represents a shared aspiration for a world where the fundamental rights of every individual are respected and upheld.