Native Plant Landscaping: Cultivating Biodiversity in Yards
Adopting native plant landscaping transforms a conventional yard into a vibrant ecosystem, fostering local biodiversity and contributing to environmental health. This approach involves selecting plants indigenous to a specific region, which are naturally adapted to the local climate and soil conditions. Beyond their ecological benefits, native plants often require less maintenance, water, and fewer chemical treatments compared to non-native species, making them a sustainable choice for homeowners seeking to enhance their outdoor spaces.
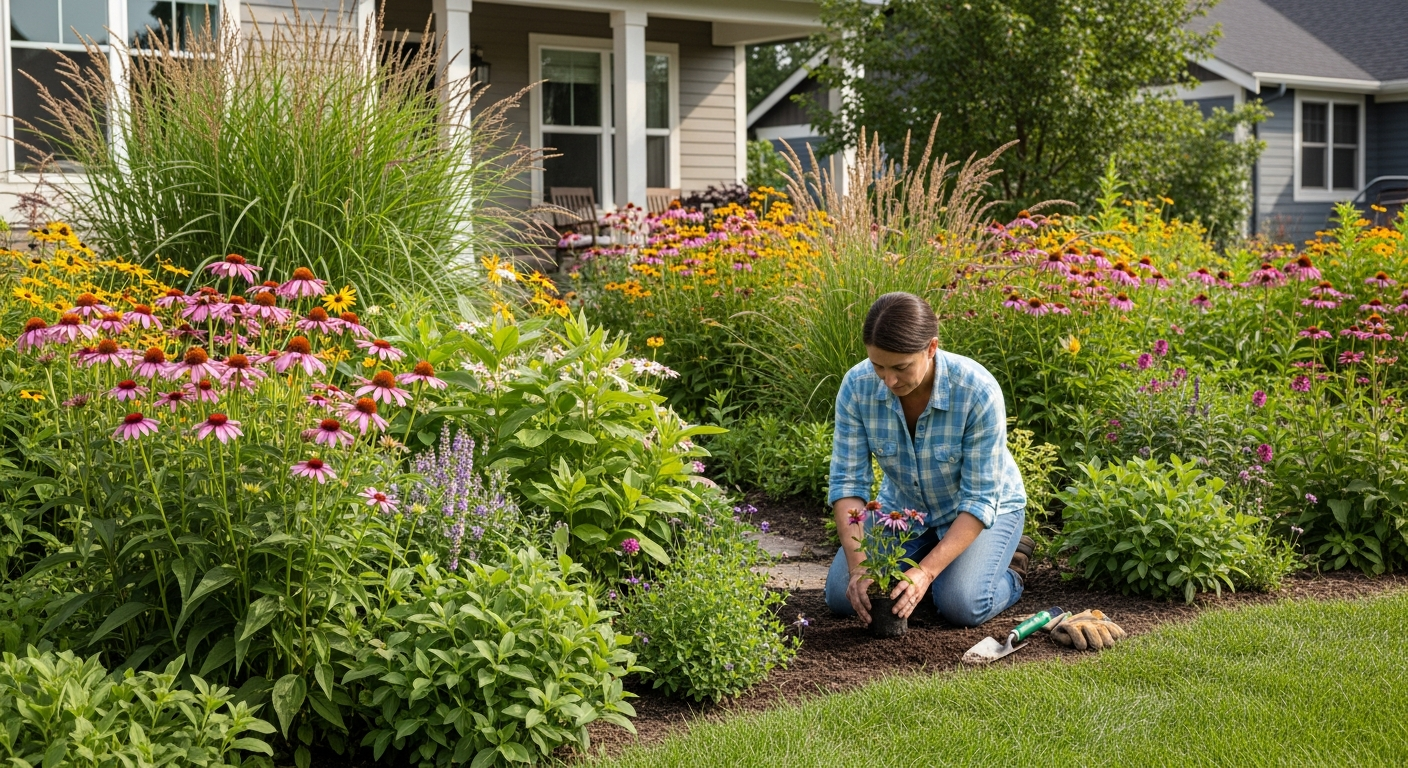

Native plant landscaping is an increasingly popular and impactful way to connect individual properties with broader ecological systems. By choosing plants that have evolved alongside local wildlife, gardeners can provide essential food, shelter, and breeding grounds for pollinators, birds, and other beneficial organisms. This practice extends beyond mere aesthetics, contributing significantly to water conservation, soil health, and a reduction in the use of pesticides and fertilizers, aligning with broader goals of environmental stewardship and sustainability.
Understanding Native Plants and Local Ecosystems
Native plants are species that occur naturally in a particular region without human introduction. These plants have adapted over millennia to the specific environmental conditions of their area, including climate, soil type, and interactions with local wildlife. Integrating them into your garden supports the entire local ecosystem by providing a reliable food source and habitat for insects, birds, and other animals. This eco-friendly approach strengthens the natural food web and promotes sustainability by reducing the need for external inputs like irrigation and synthetic chemicals, which often harm the environment and local plants.
Designing Your Native Plant Garden
Effective design is crucial for creating a native plant garden that is both ecologically beneficial and visually appealing. Begin by observing your site’s conditions, including sunlight exposure, soil type, and moisture levels. Group plants with similar requirements together to ensure their success. Consider creating layers, mimicking natural habitats, with groundcovers, shrubs, and small trees to provide diverse niches for wildlife. Thinking about color, texture, and bloom times throughout the seasons will enhance the aesthetics of your landscaping while maximizing its ecological value. This thoughtful gardening approach can transform any outdoor area into a thriving natural haven.
Benefits of Native Plant Landscaping for Home and Environment
Embracing native plant landscaping offers numerous advantages for both the homeowner and the environment. From an ecological perspective, these gardens significantly boost biodiversity by attracting and supporting local wildlife, crucial for pollination and pest control. For homeowners, native gardens often lead to increased efficiency in resource use; they typically require less water once established, reducing utility bills and conserving a precious resource. Furthermore, the reduced need for pesticides and fertilizers means less chemical exposure around your home and living spaces, contributing to a healthier environment. The natural beauty and lower maintenance can also enhance the comfort and enjoyment of your outdoor areas, making them more resilient and self-sustaining.
Selecting Native Plants for Your Area
Choosing the right plants for your native garden involves understanding your specific ecoregion and local conditions. Resources such as local botanical gardens, native plant societies, and university extension offices can provide lists of species appropriate for your area. When sourcing plants, prioritize nurseries that specialize in native species and avoid those treated with systemic pesticides, which can harm beneficial insects. Focusing on species that thrive in your urban or suburban environment ensures their long-term success and minimizes maintenance. Cultivating these indigenous species contributes not only to ecological health but also to a sense of wellness by fostering a deeper connection with the natural world.
Maintenance and Long-Term Care for Native Gardens
While native gardens are known for their low maintenance, some care is essential, especially during their establishment period. Initial watering may be necessary to help plants settle in, but once established, many native species are drought-tolerant and require minimal supplemental irrigation. Weeding is important in the early stages to prevent non-native invasive species from outcompeting young native plants. Pruning can be done to maintain plant health and shape, but generally, a more natural, less manicured look is preferred. Allowing spent flower stalks and leaf litter to remain through winter provides crucial habitat for overwintering insects, further enhancing the sustainability of your gardening efforts and enriching the greenery of your yard.
Native plant landscaping offers a compelling opportunity to create beautiful, resilient, and ecologically rich outdoor spaces. By aligning our gardening practices with nature’s own designs, we can foster vibrant ecosystems right in our yards, contributing to local biodiversity and broader environmental health. This approach not only provides a haven for wildlife but also creates a more sustainable and enjoyable environment for those who cultivate it, demonstrating how individual actions can collectively support a healthier planet.