Maximizing Green Space: Urban Garden Solutions
Urban environments, often characterized by limited space and hardscapes, present unique challenges for individuals aspiring to integrate nature into their daily lives. Despite these constraints, the desire for greenery and a connection to the natural world persists, leading to innovative approaches in urban gardening. This article explores various practical and aesthetic solutions that enable city dwellers to cultivate vibrant green spaces, transforming compact areas into flourishing habitats. From balconies to rooftops and even interior corners, the potential for urban greening is extensive, offering numerous benefits for well-being and environmental sustainability.
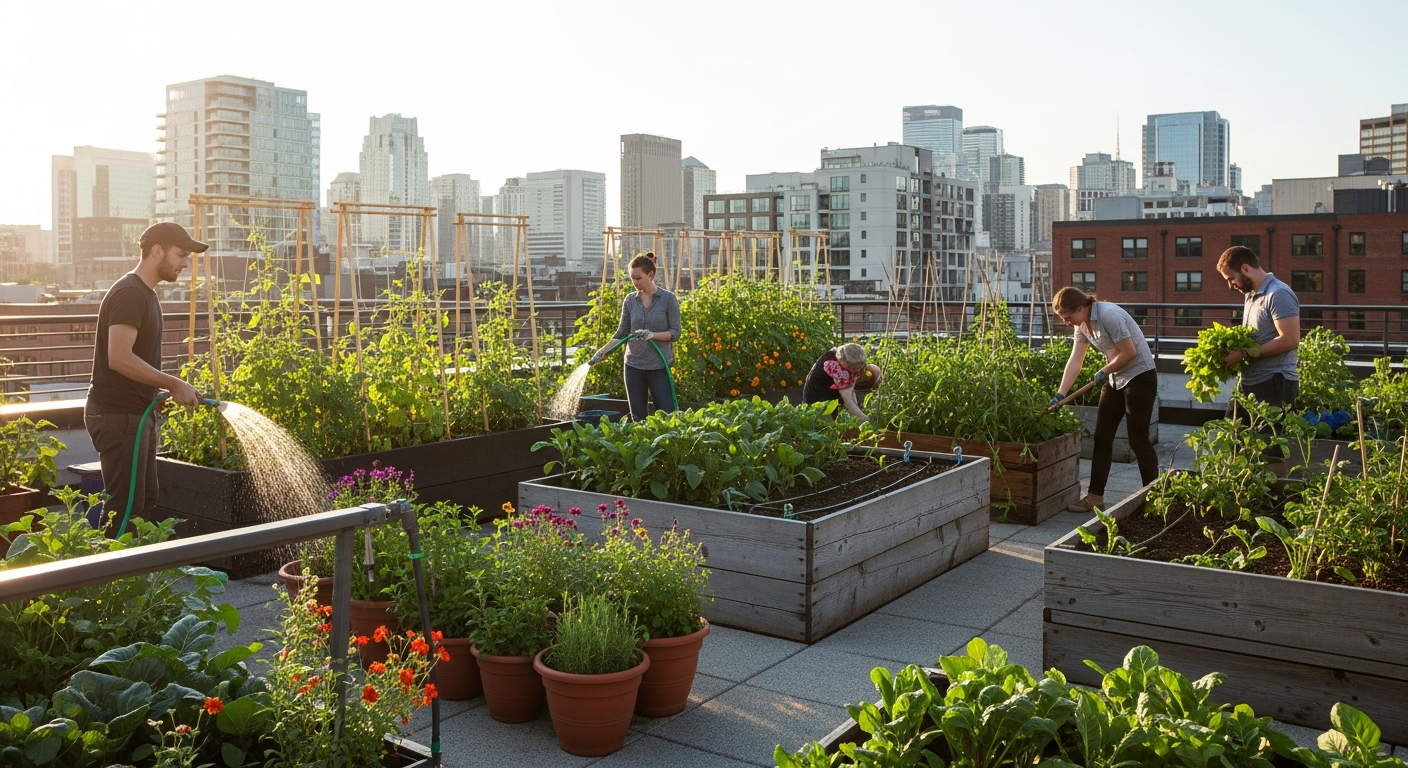

What are Effective Strategies for Urban Gardening?
Effective urban gardening strategies focus on optimizing limited areas to cultivate plants. Container gardening is a foundational technique, utilizing pots, grow bags, and planters of various sizes to grow a wide array of plants, from herbs and vegetables to ornamental flowers. Vertical gardening systems, such as wall-mounted planters, tiered shelves, and hanging baskets, are excellent for maximizing space on balconies, patios, and even interior walls. These systems allow gardeners to utilize vertical dimensions, significantly increasing planting capacity without requiring extensive ground area. Raised garden beds are another popular option, particularly for rooftops or paved yards, providing controlled growing environments with improved soil drainage and easier access for maintenance. Strategic placement of plants, considering sunlight exposure and growth habits, is crucial for success in any urban setting.
How Can Design Elements Enhance Small Outdoor Areas?
Thoughtful design is essential for transforming small outdoor areas into functional and inviting green spaces. Landscaping in urban settings often involves creative solutions like modular decking, compact furniture, and multi-functional planters that double as seating. Incorporating mirrors can create an illusion of greater depth, making a small balcony or patio feel more expansive. The choice of plants also plays a significant role; selecting species with varied textures, heights, and colors can add visual interest without overcrowding the space. Strategic lighting, such as string lights or solar-powered lanterns, extends the usability of the area into the evening, enhancing the overall ambiance. The goal is to create a cohesive and aesthetically pleasing environment that complements the surrounding architecture while providing a serene outdoor living experience.
Integrating Plants into Interior Spaces for Urban Dwellers
For those with minimal or no outdoor access, integrating plants into interiors offers a viable solution for urban greenery. Indoor plants not only enhance decor but also contribute to improved air quality and a sense of well-being. Selecting the right plants for interior conditions, considering light levels, humidity, and available space, is key. Popular choices include snake plants, pothos, ZZ plants, and various types of ferns, known for their resilience and adaptability. Creative display methods, such as hanging planters, terrariums, plant stands, and shelving units, can turn ordinary corners into lush focal points. Even small apartments can accommodate an array of plants, transforming compact interiors into vibrant, living spaces that promote a connection with nature. Regular organization and care are vital to maintain the health and aesthetic appeal of indoor plant collections.
Exploring Sustainable Practices in Urban Greening
Sustainability is a core principle in modern urban gardening and greening efforts. This involves practices that conserve resources, minimize waste, and support local ecosystems. Rainwater harvesting systems, even simple barrels, can collect water for irrigation, reducing reliance on municipal supplies. Composting kitchen scraps and garden waste enriches soil naturally, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and diverting organic material from landfills. Choosing native plants, where appropriate, can support local wildlife and require less water and maintenance once established. Employing companion planting techniques can deter pests naturally, reducing the need for pesticides. Furthermore, creating small habitats, such as bee hotels or bird feeders, contributes to biodiversity within the urban landscape, fostering a more resilient and eco-friendly environment.
DIY Approaches to Creating Urban Green Spaces
Many urban gardening solutions can be implemented through DIY projects, offering a cost-effective and personalized approach to creating green spaces. Simple renovation projects, such as converting old pallets into vertical planters or repurposing plastic bottles into self-watering systems, demonstrate creative resourcefulness. Building raised beds from reclaimed wood or constructing custom shelving for indoor plants can be rewarding projects. DIY efforts also extend to seed starting, propagating plants from cuttings, and mixing custom soil blends, all of which contribute to a deeper engagement with the gardening process. These hands-on activities not only save money but also allow individuals to tailor their green spaces precisely to their needs and aesthetic preferences, fostering a sense of accomplishment and connection to their habitat.
| Urban Garden System | Key Features | General Cost Estimation (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Container Gardening | Versatile, portable, suitable for small spaces | $50 - $300 (for pots, soil, and initial plants) |
| Vertical Garden Wall | Maximizes vertical space, aesthetic appeal | $100 - $1000+ (depending on size and system complexity) |
| Raised Garden Beds | Improved soil control, easier access, good drainage | $100 - $500 (for materials and soil, per bed) |
| Hydroponic/Aeroponic Systems | Soilless growing, faster growth, water efficient | $150 - $800+ (for basic home systems) |
| Community Garden Plot | Shared space, larger growing area, community benefits | $20 - $100 per season (for plot rental) |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Considerations for Long-Term Green Space Management
Effective long-term management of urban green spaces involves consistent care, adaptation, and planning. Regular watering, feeding, and pruning are fundamental to plant health and vitality. Monitoring for pests and diseases allows for early intervention, preventing widespread issues. As plants grow, they may require repotting or dividing, and the layout of the garden might need adjustment to accommodate changing sunlight patterns or plant sizes. Seasonal planning is also important, particularly for edible gardens, to ensure a continuous harvest. Furthermore, considering the long-term sustainability and habitat impact of the garden, such as choosing drought-tolerant plants or incorporating perennial species, contributes to a resilient and low-maintenance green space. Continual learning and experimentation are key to evolving and maintaining a thriving urban garden.
Maximizing green space in urban environments is an achievable goal through thoughtful planning, creative design, and consistent care. From small balconies to expansive rooftops, various solutions cater to different needs and spatial constraints, enabling city dwellers to cultivate personal oases. By embracing strategies like vertical gardening, sustainable practices, and DIY projects, individuals can transform concrete jungles into vibrant, living landscapes, enhancing both personal well-being and the ecological health of their urban habitat. The integration of greenery into urban living spaces not only beautifies the surroundings but also fosters a deeper connection with nature, proving that even in the densest cities, a thriving garden is within reach.